How advanced sensors can maximize electrolyzer efficiency
Hydrogen as a source of clean energy is in increasing demand. This is driving the market for hydrogen electrolyzers. To operate safely and efficiently, electrolyzers depend on the use of advanced gas monitoring sensors and analyzers, such as those manufactured by Process Sensing Technologies.
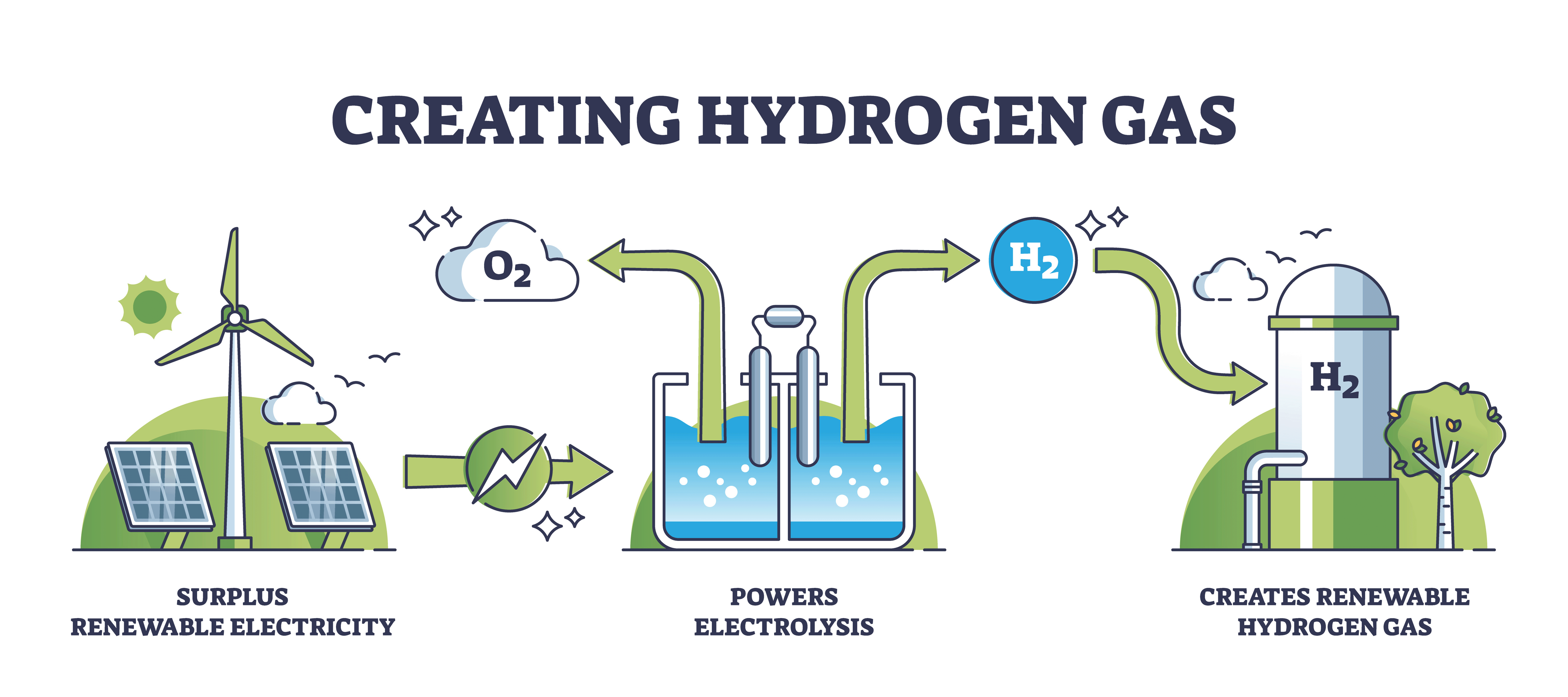
An electrolyzer works by using an electrical current to separate molecules of water into their constituent elements of oxygen and hydrogen.
Among the most common electrolyzers are Alkaline cells and Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) electrolyzers – also referred to as Polymer Electrolyte Membranes.
The latter use a semi-permeable membrane positioned between an anode and cathode. Water entering the system reacts at the anode to form oxygen, while releasing negatively charged electrons and positively charged hydrogen ions, or protons. The hydrogen protons pass through the membrane where they recombine with electrons at the cathode to form hydrogen gas.
Alkaline electrolyzers use a similar approach, with an alkaline solution such as potassium hydroxide being used as the electrolyte, into which a pair of metal electrodes are immersed. They are separated by a diaphragm, with water being split at the cathode to form H2 and release hydroxide anions that cross through the diaphragm and combine to form oxygen at the anode.
These relatively straightforward processes have considerable potential as we transition towards net zero. Research by Global Market Insights predicts that the market for hydrogen electrolyzers will grow rapidly, at a CAGR of over 24 %, from a global market value of $2.8 billion today to a staggering $78 billion as soon as 2032.
Safely optimizing electrolyzer operation
The electrolyzer cell, where water molecules are separated into their constituent atoms, forms the heart of a hydrogen electrolyzer system. However, this isn’t all that’s required to produce gas of a quality and purity that can subsequently be used as a source of energy in heating, fuel cell or transport applications.
Equally important to system design is the integration of gas purification, gas drying, compression and storage equipment, plus grid power connections and suitable gas distribution pipework. Each component has a crucial role to play in the efficient generation of high-quality hydrogen and must therefore function efficiently, reliably and, given the potentially explosive nature of hydrogen, safely. In turn, this demands the use of high-performance process monitoring, measurement and control instruments.
For example, monitoring the oxygen content in the hydrogen gas stream in an electrolyzer system is a key prerequisite for its safe operation, ideally based on accepted safety standards and operating guidelines, such as those defined under the SIL (Safety Integrity Level) model. These same oxygen concentration measurements also provide an accurate guide to the operational efficiency of the electrolyzer cell, indicate the presence of gas leaks and act as important criteria to demonstrate that gas quality and contractual obligations are being met.
Gas quality will also be affected by the presence of water vapor carried over from the electrolysis process. This necessitates the use of hydrogen dehydration, plus the use of suitable moisture or dew-point sensors to detect trace levels of moisture once the gas has passed through the drying process. Again, these measurements are crucial for system operation and optimization, and for showing that gas purity meets the required commercial and technical criteria.
Oxygen, hydrogen and dew-point measurement instruments
We’ve been developing advanced sensors and analyzers for the measurement of oxygen and water dew point in hydrogen electrolyzers for over ten years. Many of our sensors and transmitters are designed to meet the requirements for use in SIL environments, as well as being approved to a range of international safety and quality standards.
To highlight just one example from our extensive range of products, Easidew Dew-Point transmitters are fully certified for use in intrinsically safe and hazardous areas. This makes them ideal for installation at the output of hydrogen purification and drying units to ensure that the gas conforms to the required specifications. Easidew transmitters are based on our robust and proven ceramic metal-oxide sensing technology, which ensures excellent accuracy, to within ±2 °Cdp, across a wide measuring range, while giving exceptional response rates and long-term stability.
Devices such as the Easidew can be used in conjunction with our oxygen sensors and remote analyzers, providing OEMs and end users alike with reliable, cost-effective and versatile solutions to the challenges of monitoring the performance, efficiency and safety of hydrogen electrolyzers.
We are the world’s leading experts in moisture monitoring and dew-point and gas measurement. We have a range of technologies, backed by unrivalled technical and customer support. To learn more, talk to one of our application specialists today.
Hydrogen is a chemical element with the symbol ‘H’ and the atomic number ‘1’. It is the lightest and most abundant element in the universe, making up around 75 % of its elemental mass. Hydrogen has just one proton and electron, is the only element where its atoms do not contain any neutrons, and readily combines with other elements to form compounds such as water (H2O) and hydrocarbons.
Hydrogen is widely used in the production of ammonia for fertilizers, as part of the petroleum refining process and as a fuel for rockets. It is increasingly seen as a key source of clean energy: for example, when used in fuel cells, hydrogen can generate electricity with only water as a byproduct, offering an alternative to fossil fuels and thus reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Sources
Global Market InsightsRelated Blogs
How to Measure and Control Moisture in Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Using Electrolyzers for Industrial H2 Production
How to Ensure the Safety and Gas Quality of Hydrogen Electrolyzers
Related Categories
Industrial Dew-Point Transmitters, Dew-Point Sensors and Trace Moisture Sampling SystemsRelated Products
Intrinsically Safe Dew-Point Transmitter - Easidew I.S.
Dew-Point Transmitter - Michell Easidew EA2
Oxygen Analyzer - Michell XTP601
Binary Gas Analyzer for Hydrogen Monitoring - Michell XTC601
Intrinsically Safe Compact Oxygen Transmitter - Minox-i
Compressed Gas Dew Point Meter - Easidew PDP
Dryer Portable
Want to see more information like this?
Sign up to one of our Industry newsletters and you’ll receive our most-recent related news and insights all directly to your inbox!
Sign Up